
At low doses, methamphetamine also blocks the re-uptake of dopamine, but it also increases the release of dopamine, leading to much higher concentrations in the synapse (the gap between neurons), which can be toxic to nerve terminals. 38,39 Prev Next October 2019 Cite this article PDF (139. Cocaine prolongs dopamine actions in the brain by blocking the re-absorption (re-uptake) of the neurotransmitter by signaling nerve cells. At low doses, methamphetamine also blocks the re-uptake of dopamine, but it also increases the release of dopamine, leading to much higher concentrations in the synapse (the gap between neurons), which can be toxic to nerve terminals. 46Īlthough both methamphetamine and cocaine increase levels of dopamine, administration of methamphetamine in animal studies leads to much higher levels of dopamine, because nerve cells respond differently to the two drugs. Methamphetamine therefore remains in the brain longer, which ultimately leads to prolonged stimulant effects. In contrast to cocaine, which is quickly removed from and almost completely metabolized in the body, methamphetamine has a much longer duration of action, and a larger percentage of the drug remains unchanged in the body.
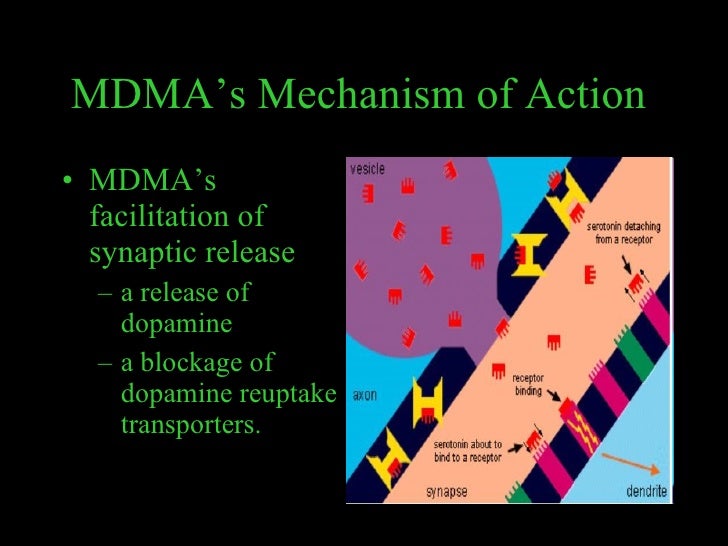
45 Although these stimulants have similar behavioral and physiological effects, there are some major differences in the basic mechanisms of how they work. The methamphetamine molecule is structurally similar to amphetamine and to the neurotransmitter dopamine, a brain chemical that plays an important role in the reinforcement of rewarding behaviors, but it is quite different from cocaine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
